The Power of Metadata in Incident Investigations
In this blog, we’ll explore how to incorporate metadata into your incident investigation diagram. But first, what exactly is an incident investigation? As the name suggests, an investigation is conducted to understand how and why things went wrong, ultimately preventing similar major incidents in future. For a deeper look into the fundamentals, check out our basics of incident investigations blog.
What is metadata?
Metadata is essentially information about data. In incident investigations, it provides key details such as date, time, owner, and condition. Metadata ensures that files are traceable and that their sources, conditions, and other relevant details are clear, supporting a more precise and efficient investigative process.
Types of metadata
- Descriptive metadata: Provides basic information, like the title, author, date created, and keywords.
- Administrative metadata: Contains details for managing a resource, such as when and how it was created, who can access it, and any rights information.
- Structural metadata: Explains how data are organised, like the table of contents for a document or the relationship between multiple files.
- Provenance metadata: Captures details on data origins—who created or modified it, when, and how.
The benefits of metadata
In practical terms, metadata makes data easier to organise, find, and understand. For incident investigations, it ensures that files are traceable and that their sources, conditions, and relevant details are clear. But metadata offers more than just organisation and retrieval — here are key benefits of metadata in incident investigations:
- Barrier Condition and Health Monitoring Tracking: Metadata logs the type and condition of each barrier, allowing investigators to monitor its status and effectiveness over time. Metadata can also provide continuous insights into barrier health, signaling when maintenance or updates might be required to keep barriers functioning optimally.
- Comprehensive Scenario View: By consolidating metadata, investigators gain a complete view of the incident, enabling them to assess risks and make informed decisions more effectively.
- Trends Analysis: Metadata can capture details over time, making it possible to identify patterns across multiple incidents, which helps in proactive risk management and the prevention of recurring issues.
- Audit and Compliance Support: Metadata keeps a record of changes and user interactions, assisting investigators in meeting regulatory requirements and demonstrating due diligence during audits.
How to incorporate metadata into an incident investigation
Did you know you can enhance your incident investigation by adding metadata? Here are some effective ways to do it:
- Capture metadata consistently during data collection: Begin by using investigation tools that can capture essential metadata when collecting files, photos, and documents. This initial step ensures every data element is tagged with basic elements like timestamps, location, and file format without manual effort. For instance, tools such as Incident Insight support capturing metadata for witness statements, photos, and logs.
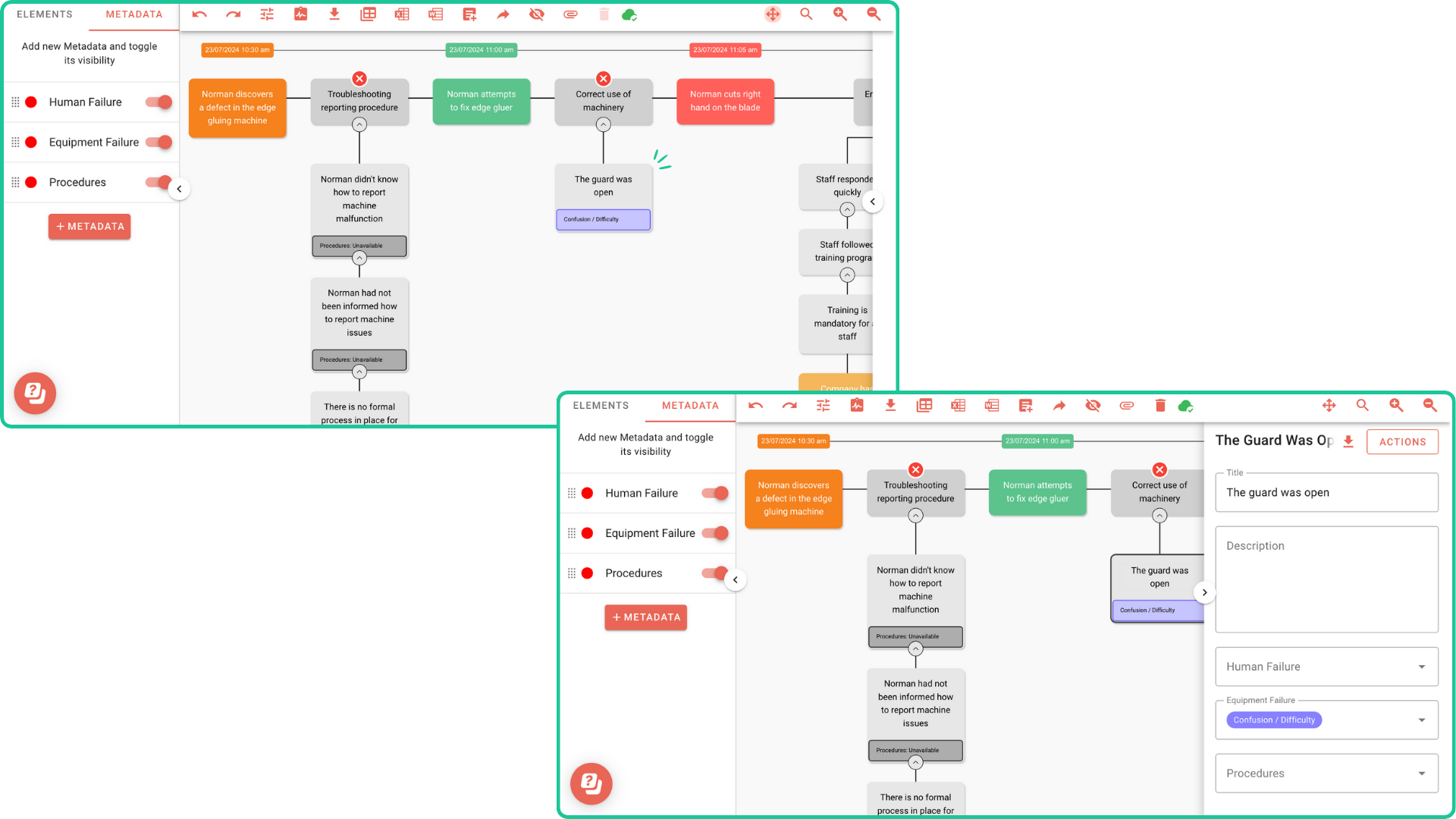
- Standardise metadata fields: Develop a standardised template to make sure every investigator captures the same metadata fields to maintain consistency across investigations. Standard fields can include author, date, location, equipment type, barrier condition, and more. In Incident Insight, we have default metadata templates such as Human Failure, Equipment Failure, and Procedures as seen in Figure 1. You can add and customise your own metadata as well.
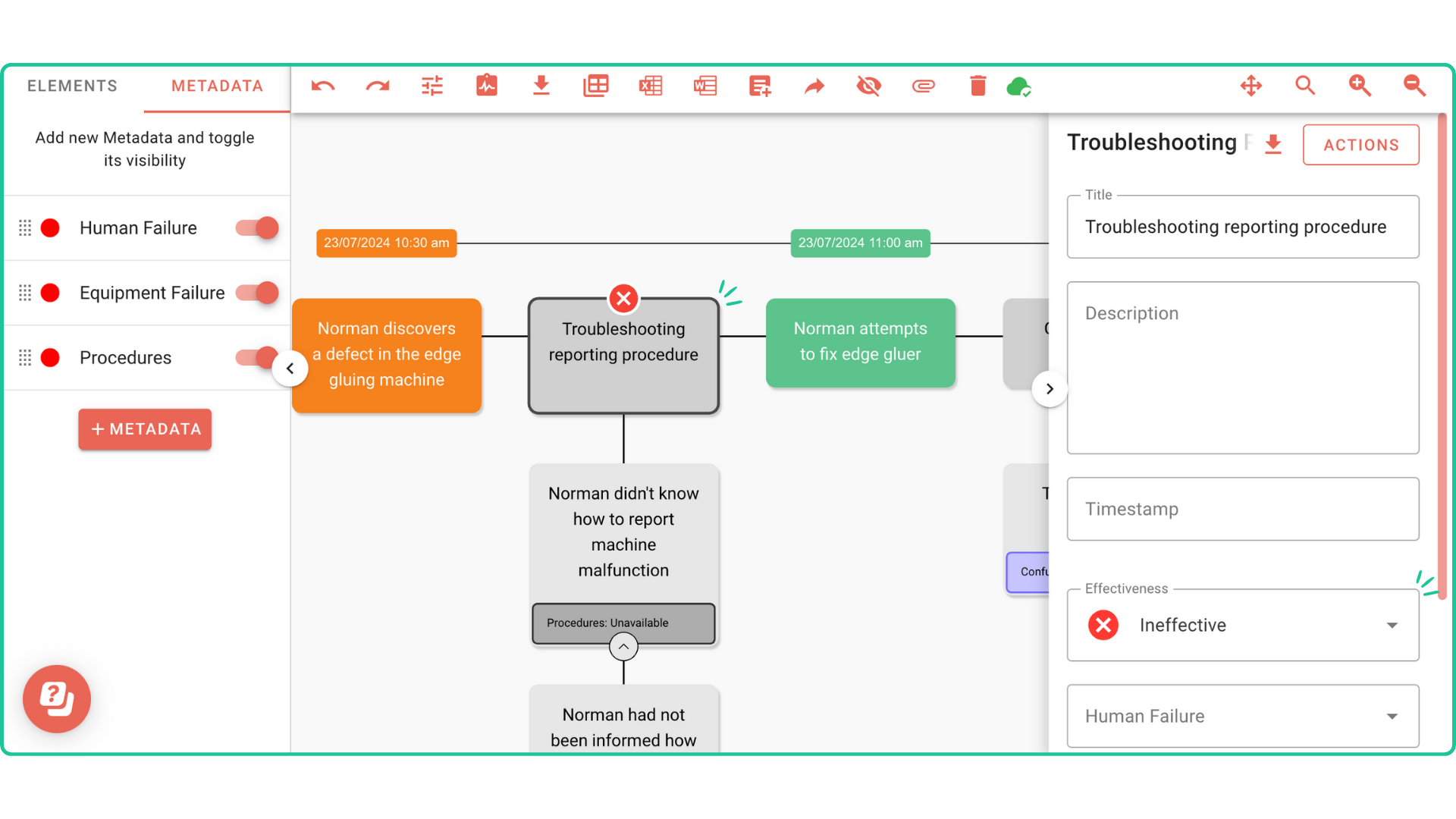
- Use metadata to track barrier health and effectiveness: Assign tags that record each barrier’s condition. This allows investigators to monitor the health of barriers over time and identify and degradation in effectiveness. This also makes it easier to see at a glance if any have failed previously or need maintenance, adding a preventative layer to the investigation process. In Figure 2, it is easy to spot what barriers health are compromised with the “x” mark. In Incident Insight, mark your barrier’s effectiveness by choosing between partially effective, effective, and not effective.
- Continuously update metadata during investigations: As new findings surface, update metadata fields to keep records current. For example, if new evidence or insights arise, ensure that any associated metadata —such as date modified, source, or other notes—is adjusted. Consistent updates help ensure that the final investigation report reflects the complete, up-to-date picture of the incident.
Conclusion
With Incident Insight, capturing and managing metadata makes the incident investigation process more accurate and efficient. It also simplifies uncovering both immediate and root causes. Want to learn how to seamlessly add metadata into your investigations? Book a demo at your convenience and see Incident Insight in action!




